

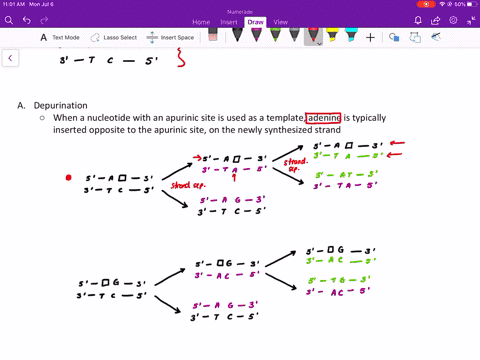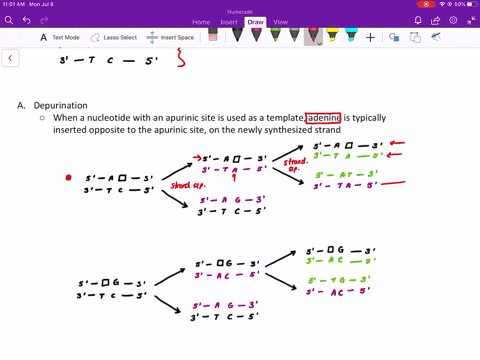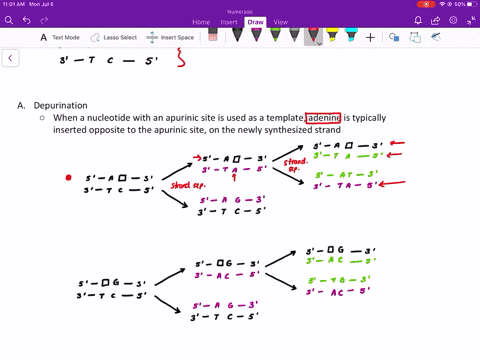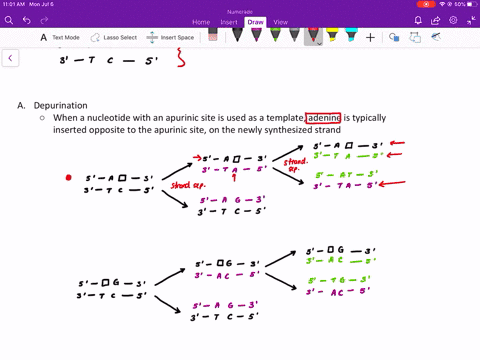
Comme pour la plupart des autres protéines séquencées de la couche S, la RsaA ne contenait pas de résidu de cystéine. Mise à part l'aspartate, la proportion des acides aminés chargés était relativement faible expliquant ainsi que la protéine est particulièrement acide avec un pI prévu à 3,46. La composition en acides aminés prédite pour RsaA était inhabituelle à cause d'une prédominance en petits résidus neutres. À l'exception de l'élimination du résidu mèthionine initial, la protéine n'a pas subi de maturation par clivage pour produire la protéine mature. Ainsi aucune maturation par clivage de la portion carboxyle de la protéine RsaA n'a eu lieu durant l'exportation. Le clivage par des protéases de la protéine RsaA mature et le séquencage des acides aminés des peptides recouvrables a produit deux peptides : un s'allignant avec une région localisée approximativement jusqu'au deux tiers de la séquence peptidique prédite et un deuxième correspondant à l'extrémité carboxyterminale prédite.
#Nucleotide sequence analysis code#
Ce gène rsaA code pour une protéine de 1026 acides aminés et de poids moléculaire de 98 132. Nous avons déterminé la séquence nucléotidique complète du gène rsaA qui code la protéine (RsaA) présente dans la couche de surface (S) paracrystalline chez Caulobacter crescentus CB15A. Key words: Caulobacter crescentus, surface layer, nucleotide sequence, rsaA, calcium. RsaA protein also shared some homology with 10 other S-layer proteins, with the Campylobacter fetus S-layer protein scoring highest. Those present in the RsaA protein may perform a similar function, since S-layer assembly and surface attachment requires calcium. These repeats are implicated in the binding of calcium for proper structure and biological activity of these proteins. Of particular interest was a specific region of the RsaA protein that was homologous to the repeat regions of glycine and aspartate residues found in several proteases and hemolysins. However, RsaA protein shared measurable homology with some exported proteins of other bacteria, including the hemolysins. A homology scan of the Swiss Protein Bank 17 produced no close matches to the predicted RsaA sequence. As with most other sequenced S-layer proteins, RsaA contained no cysteine residues. Excepting aspartate, charged amino acids were in relatively low proportion, resulting in an especially acidic protein, with a predicted pI of 3.46.

The predicted RsaA amino acid profile was unusual, with small neutral residues predominating. Thus, no cleavage processing of the carboxy portion of the RsaA protein occurred during export, and with the exception of the removal of the initial methionine residue, the protein was not processed by cleavage to produce the mature protein. Protease cleavage of mature RsaA protein and amino acid sequencing of retrievable peptides yielded two peptides: one aligned with a region approximately two-thirds the way into the predicted amino acid sequence and the second peptide corresponded to the predicted carboxy terminus. The rsaA gene encoded a protein of 1026 amino acids, with a predicted molecular weight of 98 132. The entire nucleotide sequence of the rsaA gene, encoding the paracrystalline surface (S) layer protein (RsaA) of Caulobacter crescentus CB15A, was determined.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
